Table of Contents
- Importance of Hands-On Training
- Real-World Scenarios
- Technological Advancements in Training
- Collaborative Training Initiatives
- Balancing Theory and Practice
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Conclusion
Practical experience is a cornerstone in developing the skills and confidence necessary for first responders. While theoretical knowledge provides a foundation, the ability to react quickly under pressure, make critical decisions, and handle life-threatening situations effectively comes from immersive, hands-on training. Firefighters and EMTs benefit greatly from simulations, live drills, and real-world scenario exercises that replicate the unpredictability of emergencies. These experiences not only build technical proficiency but also foster teamwork, situational awareness, and mental resilience —essential traits for saving lives in high-stress environments.
For those entering the field, programs like an emergency medical responder course Texas offer structured, hands-on opportunities to practice essential procedures, from patient assessment to emergency care techniques. Such courses bridge classroom learning with practical application, ensuring trainees are prepared to respond confidently and efficiently when emergencies arise.
Importance of Hands-On Training
Responding to emergency calls requires more than theoretical understanding—it requires instinctive action. Hands-on training develops the critical reflexes and muscle memory that professionals rely on during split-second, life-or-death decisions. Physical drills cultivate teamwork, stress management, and operational efficiency, all of which are proven to improve outcomes in the most time-sensitive situations. According to the National Fire Protection Association, realistic hands-on exercises can significantly reduce errors and increase safety during actual emergencies.
Real-World Scenarios
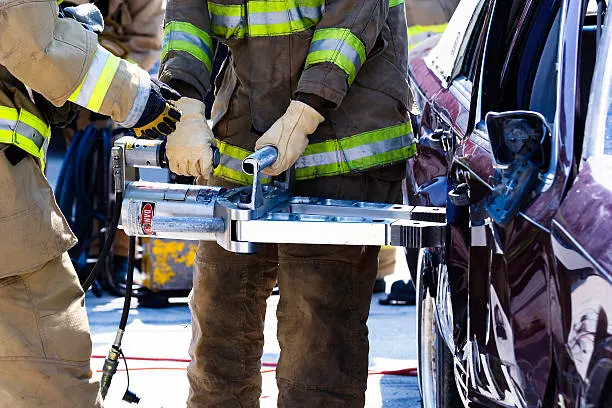
Scenario-based training exposes firefighters and EMTs to rare but high-impact incidents they may encounter. In Stone County, Mississippi, firefighters tackled a hands-on rescue simulation that involved dismantling a wrecked school bus, a learning opportunity that reinforced advanced extrication techniques. By practicing on a real vehicle, trainees learned how to maneuver around tangled metal and confined spaces while prioritizing the safety of victims. Drills like these bring abstract learning to life, helping responders remain calm, methodical, and adaptable in chaotic environments.
Technological Advancements in Training
Modern technology has transformed emergency responder training by allowing simulations of dangerous scenarios without real-world risks. AR and VR immerse trainees in fires, spills, and mass casualty events, while wearable sensors and heads-up displays boost spatial awareness, navigation, and team communication.
Collaborative Training Initiatives
Bringing together personnel from different agencies fosters the sharing of expertise and the alignment of protocols, which is essential during large-scale emergencies. In Greater Cincinnati, firefighters from multiple counties jointly trained in fire investigation, learning new methods for determining the origins and patterns of blazes. These collaborative exercises enhance investigative skills and boost interoperability and coordination among multiple agencies during urgent situations.
Balancing Theory and Practice
While e-learning and classroom instruction lay the groundwork for technical knowledge, they must be integrated with authentic hands-on experience for optimal readiness. Online resources allow fire and EMS personnel to learn at their own pace and revisit crucial content. Still, nothing can replace the physical and emotional immersion of on-the-ground exercises. According to a review in Firehouse Magazine, the hybrid approach—combining e-learning with skills-focused drills produces the most adaptable and confident responders.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The fields of firefighting and emergency medical response are constantly evolving. Departments that prioritize regular, updated training see improved readiness and resilience. Ongoing skills refreshers and scenario-based drills keep responders prepared for unforeseen situations.
Conclusion
Effective emergency response relies on combining theoretical knowledge with practical experience. Immersive training enables firefighters and EMTs to respond accurately and calmly in high-pressure situations, thereby protecting the lives of those they serve. As new challenges and technologies emerge, flexible, collaborative, and scenario-driven training will remain essential in developing resilient emergency response teams.
Also Read- Tom Holland’s On-Screen Roles, Body Transformation & Personal Life